[ad_1]
Engineers from Duke College and the Institut de Physique de Good in France have developed a brand new technique to determine objects utilizing microwaves that improves accuracy whereas decreasing the related computing time and energy necessities.
The system might present a lift to object identification and velocity in fields the place each are important, resembling autonomous autos, safety screening and movement sensing.
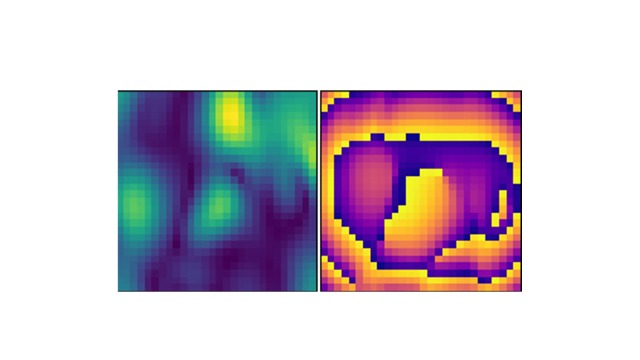
The brand new machine-learning method cuts out the intermediary, skipping the step of making a picture for evaluation by a human and as an alternative analyzes the pure knowledge immediately. It additionally collectively determines optimum settings that reveal an important knowledge whereas concurrently discovering what an important knowledge truly is. In a proof-of-principle examine, the setup accurately recognized a set of 3D numbers utilizing tens of measurements as an alternative of the lots of or 1000’s usually required.
The outcomes seem on-line on December 6 within the journal Superior Science and are a collaboration between David R. Smith, the James B. Duke Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Pc Engineering at Duke, and Roarke Horstmeyer, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Duke.
“Object identification schemes usually take measurements and go to all this hassle to make a picture for individuals to have a look at and admire,” stated Horstmeyer. “However that is inefficient as a result of the pc does not must ‘look’ at a picture in any respect.”
“This method circumvents that step and permits this system to seize particulars that an image-forming course of may miss whereas ignoring different particulars of the scene that it does not want,” added Aaron Diebold, a analysis assistant in Smith’s lab. “We’re principally attempting to see the item immediately from the eyes of the machine.”
Within the examine, the researchers use a metamaterial antenna that may sculpt a microwave wave entrance into many various shapes. On this case, the metamaterial is an 8×8 grid of squares, every of which comprises digital constructions that enable it to be dynamically tuned to both block or transmit microwaves.
For every measurement, the clever sensor selects a handful of squares to let microwaves cross by way of. This creates a novel microwave sample, which bounces off the item to be acknowledged and returns to a different comparable metamaterial antenna. The sensing antenna additionally makes use of a sample of energetic squares so as to add additional choices to form the mirrored waves. The pc then analyzes the incoming sign and makes an attempt to determine the item.
By repeating this course of 1000’s of instances for various variations, the machine studying algorithm ultimately discovers which items of knowledge are an important in addition to which settings on each the sending and receiving antennas are the very best at gathering them.
“The transmitter and receiver act collectively and are designed collectively by the machine studying algorithm,” stated Mohammadreza Imani, analysis assistant in Smith’s lab. “They’re collectively designed and optimized to seize the options related to the duty at hand.”
“If you understand your process, and you understand what kind of scene to anticipate, you might not must seize all the knowledge attainable,” stated Philipp del Hougne, a postdoctoral fellow on the Institut de Physique de Good. “This co-design of measurement and processing permits us to utilize all of the a priori information that we’ve got in regards to the process, scene and measurement constraints to optimize your entire sensing course of.”
After coaching, the machine studying algorithm landed on a small group of settings that might assist it separate the information’s wheat from the chaff, reducing down on the variety of measurements, time and computational energy it wants. As a substitute of the lots of and even 1000’s of measurements usually required by conventional microwave imaging methods, it might see the item in lower than 10 measurements.
Whether or not or not this stage of enchancment would scale as much as extra difficult sensing purposes is an open query. However the researchers are already attempting to make use of their new idea to optimize hand-motion and gesture recognition for next-generation laptop interfaces. There are many different domains the place enhancements in microwave sensing are wanted, and the small measurement, low price and simple manufacturability of these kinds of metamaterials make them promising candidates for future gadgets.
“Microwaves are perfect for purposes like hid menace detection, figuring out objects on the street for driverless automobiles or monitoring for emergencies in assisted-living services,” stated del Hougne. “When you consider all of those purposes, you want the sensing to be as fast as attainable, so we hope our method will show helpful in making these concepts dependable realities.”
Reference: Dorison, C. A., Wang, Ok., Rees, V. W., Kawachi, I., Ericson, Ok. M. M., & Lerner, J. S. (2019). Disappointment, however not all adverse feelings, heightens addictive substance use. Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909888116
This text has been republished from the next supplies. Observe: materials could have been edited for size and content material. For additional data, please contact the cited supply.
[ad_2]